To insert a deleted identity row back into a SQL Server table while preserving the specific identity value, you need to temporarily enable IDENTITY_INSERT for the table.
- Enable
IDENTITY_INSERTon the table. - Insert the row with the specific identity value.
- Disable
IDENTITY_INSERTon the table.
Assume you have a table named td_employee with an identity column EmployeeID and other columns like FirstName, LastName, and Email.
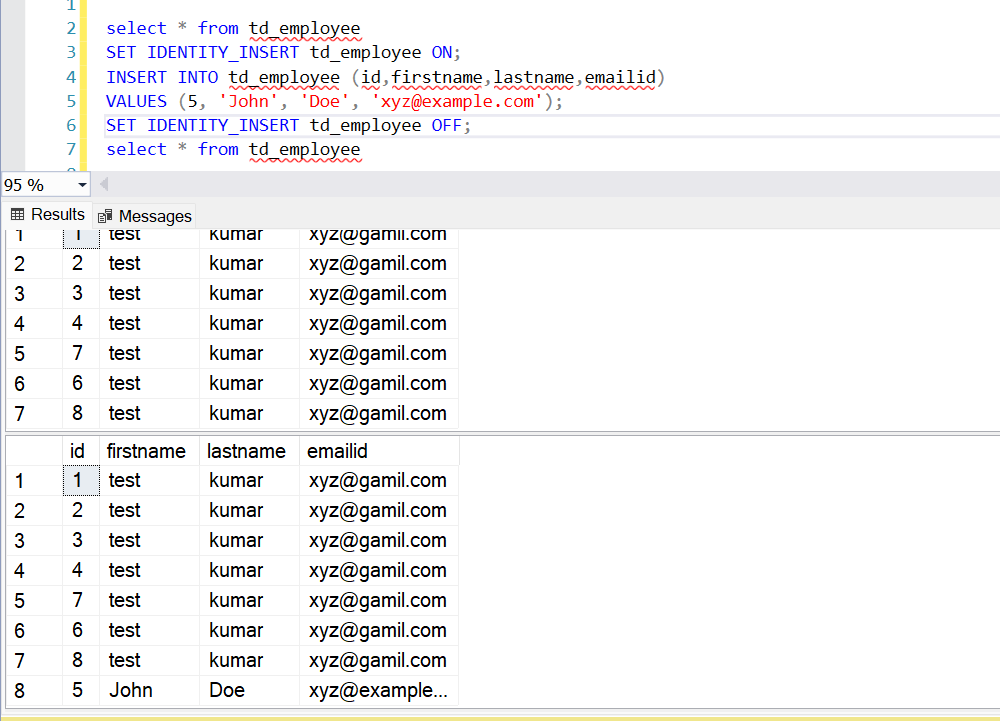
Note:
- Ensure Unique Identity Values: Make sure the identity value you’re inserting does not already exist in the table, as this would cause a primary key violation.
- Performance Impact: Avoid keeping
IDENTITY_INSERTon for extended periods, as it can affect performance and concurrency. - Permissions: You need appropriate permissions to enable/disable
IDENTITY_INSERTand perform inserts.
Explanation:
- SET IDENTITY_INSERT [TableName] ON: This command allows you to explicitly insert values into the identity column of the table.
- INSERT INTO [TableName] ([ColumnList]) VALUES ([Values]): This is the standard SQL insert statement, but with the identity column explicitly included in the column list.
- SET IDENTITY_INSERT [TableName] OFF: This command disables the ability to insert explicit values into the identity column, returning control of the identity column to SQL Server.
By following these steps, you can reinsert a deleted row with its original identity value, ensuring data integrity and continuity in your table.